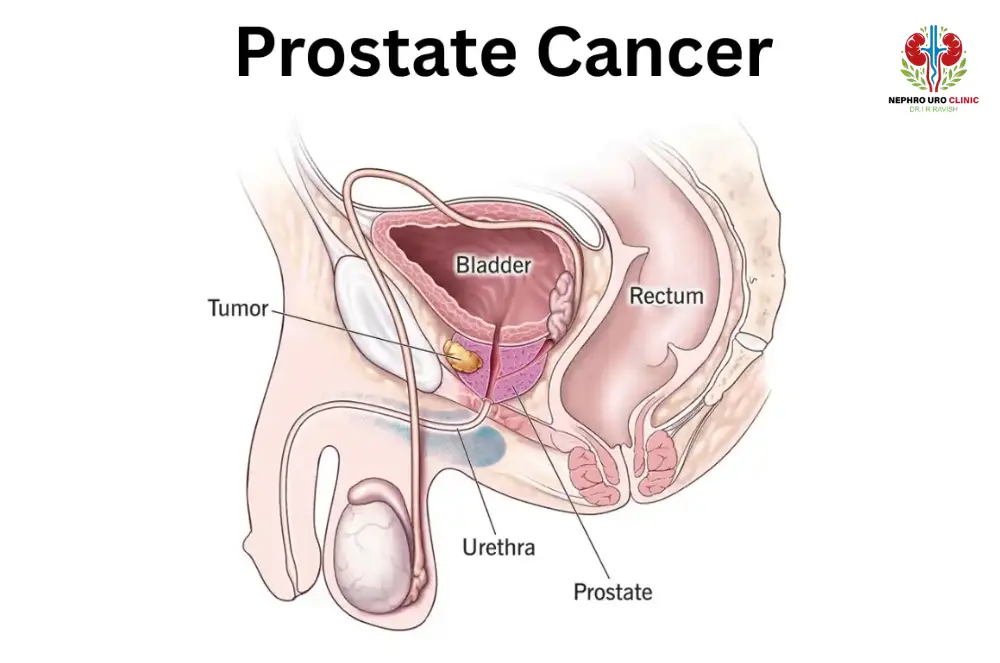
Prostate cancer begins in the small gland that produces seminal fluid, a vital part of the male reproductive system. In its early stages, it often grows slowly and remains confined—but when it advances, the effects can be devastating. For those navigating its final stages, understanding the signs you are dying of prostate cancer is both sobering and essential. This knowledge can help families prepare, offer better care, and bring peace during life’s most vulnerable chapter.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops in the small gland located below the bladder, responsible for producing seminal fluid. Recognizing how to know if prostate cancer often involves identifying symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent night-time urination, blood in the urine, or pelvic discomfort, followed by PSA testing, digital rectal examination, imaging, and biopsy for confirmation. The disease is classified by Gleason score and stage, which significantly influence both treatment planning and prognosis.
Prostate cancer stages life expectancy varies widely—localized cancers can have decades of survival potential, while advanced cases often have a limited outlook. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone-blocking therapy, chemotherapy, and advanced targeted medications. In localized disease, prostate cancer treatment success rates are high, but advanced stages focus more on symptom control and life extension rather than cure.
Aggressive prostate cancer symptoms, such as rapid PSA increases, severe bone pain, or significant weight loss, may indicate early metastasis and require urgent medical attention. Though rare, symptoms of prostate cancer in women can occur when cancers develop in the Skene’s glands, presenting with urinary changes and pelvic pain similar to male cases.
How Does Prostate Cancer Progress in its Final Stages?
- System-wide changes: In end stage prostate cancer, the body undergoes muscle wasting, immune decline, and energy loss. How does prostate cancer kill you in the end often relates to organ failure rather than the primary tumor.
- Bone metastasis and pain: Spread to the bones can cause fractures, immobility, and intense pain. This is one of the most common aggressive prostate cancer symptoms in advanced stages.
- Lymphatic effects: Enlarged lymph nodes can cause swelling, discomfort, and difficulty with bladder or bowel functions, worsening as cancer advances.
- Major body function decline: Fatigue, anemia, and weakness progress steadily, limiting daily activity.
- Vital organ impact: Metastases to lungs or liver can cause breathing difficulties or jaundice. These are critical points when prostate cancer stages life expectancy shortens considerably.
- Palliative care approach: Care shifts to comfort-focused strategies to improve quality of life.
- Pain management and support: Opioids, nerve blocks, and targeted therapies help relieve severe bone and nerve pain.
- Comprehensive care team: Doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, dietitians, and counselors work together to address all needs during end stage prostate cancer.
Key Signs You Are Dying of Prostate Cancer
Urinary problems
Difficulty starting urination, weak or interrupted flow, dribbling, or complete retention are advanced signs you are dying of prostate cancer. The tumor often compresses or blocks the urethra, making bladder emptying painful or impossible. In severe stages, catheterization may be required, and urinary tract infections can develop, further weakening the patient.
Bone pain
Persistent, deep pain in the back, hips, ribs, or legs is one of the strongest signs you are dying of prostate cancer. This usually results from metastases spreading to the bone marrow, causing fractures, nerve compression, and reduced mobility. Pain may worsen at night or with minimal movement, requiring strong opioids for relief.
Weakness
Severe fatigue, muscle wasting, and loss of energy occur as cancer spreads and the body struggles to sustain itself. Weakness may make even simple tasks exhausting, forcing the patient to remain bedridden. This profound decline is often linked to anemia, weight loss, and the cancer’s impact on metabolic function.
Breathing issues
Shortness of breath, wheezing, or labored breathing are signs of advanced prostate cancer that has spread to the lungs or caused fluid buildup in the chest (pleural effusion). This reduces oxygen levels and can make talking or lying flat uncomfortable. In final stages, supplemental oxygen may be needed.
Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin and eyes is a late sign of prostate cancer that has metastasized to the liver. This occurs when tumor growth obstructs bile ducts or destroys liver tissue, leading to toxin buildup. Jaundice is often accompanied by itching, abdominal swelling, and dark urine, signaling a critical decline.
Slowed blood flow
Cold hands and feet, bluish skin, and a drop in blood pressure are clear indicators the circulatory system is shutting down. This is part of the body’s natural process of redirecting blood to vital organs during the dying phase. Patients may feel extremely cold despite blankets or heating.
Loss of appetite
One of the hallmark signs you are dying of prostate cancer is a severe decline in hunger. The patient may refuse food entirely, leading to rapid weight loss and muscle breakdown. This is caused by both cancer-related changes in metabolism and reduced digestive function in the final stages.
Digestive changes
Advanced prostate cancer can cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, or bowel obstruction due to pressure from tumors or reduced physical activity. Swelling in the abdomen from ascites (fluid buildup) can also impair digestion, making eating and drinking uncomfortable.
Sleep changes
As the end approaches, patients often experience excessive sleepiness or restlessness. Some may sleep almost constantly, while others become agitated and unable to rest. These changes are part of the body’s shutdown process, influenced by reduced oxygen supply and metabolic slowdown.
Confusion
Disorientation, memory loss, or a reduced ability to recognize familiar people are late signs of end-stage prostate cancer. This may result from brain metastases, low oxygen levels, or buildup of toxins in the blood. In the final days, awareness often fades completely before passing.
How to Provide Comfort in the Final Stages
- Physical comfort: Pain relief, pressure-relieving mattresses, and careful positioning are key. Managing these needs can ease many signs you are dying of prostate cancer.
- Breathing comfort: Fans, oxygen therapy, and calming techniques reduce shortness of breath.
- Nutritional needs: Small, preferred meals and good mouth care support dignity when eating becomes difficult.
- Stage-specific care: Interventions differ between early, advanced, and final phases of the disease, aligning with prostate cancer treatment success rates goals in earlier stages and comfort in later stages.
- Emotional and spiritual support: Counseling and community or spiritual guidance reduce anxiety.
- Hospice care: Hospice teams address pain, breathing issues, and emotional well-being at home or in care facilities.
- Caregiver support: Rest, assistance, and emotional counseling prevent burnout.
- Communication support: Open discussions about signs you are dying of prostate cancer and care preferences ensure treatment aligns with personal values.
What to Expect in the Final Stages
- In rare cases, symptoms of prostate cancer in women at advanced stages can mirror those in men, requiring similar palliative approaches.
- The final phase is marked by fatigue, appetite loss, confusion, and increased sleep. These signs you are dying of prostate cancer help families recognize when to focus solely on comfort.
- How does prostate cancer kill you in the end often comes down to organ failure, severe infection, or complications from widespread metastasis.
- Prostate cancer treatment success rates are high for early-stage disease but drop significantly with distant metastases, making prostate cancer stages life expectancy much shorter.
- Recognizing these shifts early helps families prepare for end stage prostate cancer care needs and focus on symptom management.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs you are dying of prostate cancer is emotionally difficult but medically important. Understanding the progression—from fatigue and pain to confusion and organ failure—can help families prepare and make compassionate decisions. End-stage care focuses on comfort, dignity, and emotional support. Every experience is unique, but informed awareness ensures no one faces it alone.
Speak with a medical professional to explore the best path forward with clarity and care.
Read also How to Get Rid of Kidney Stone Pain.