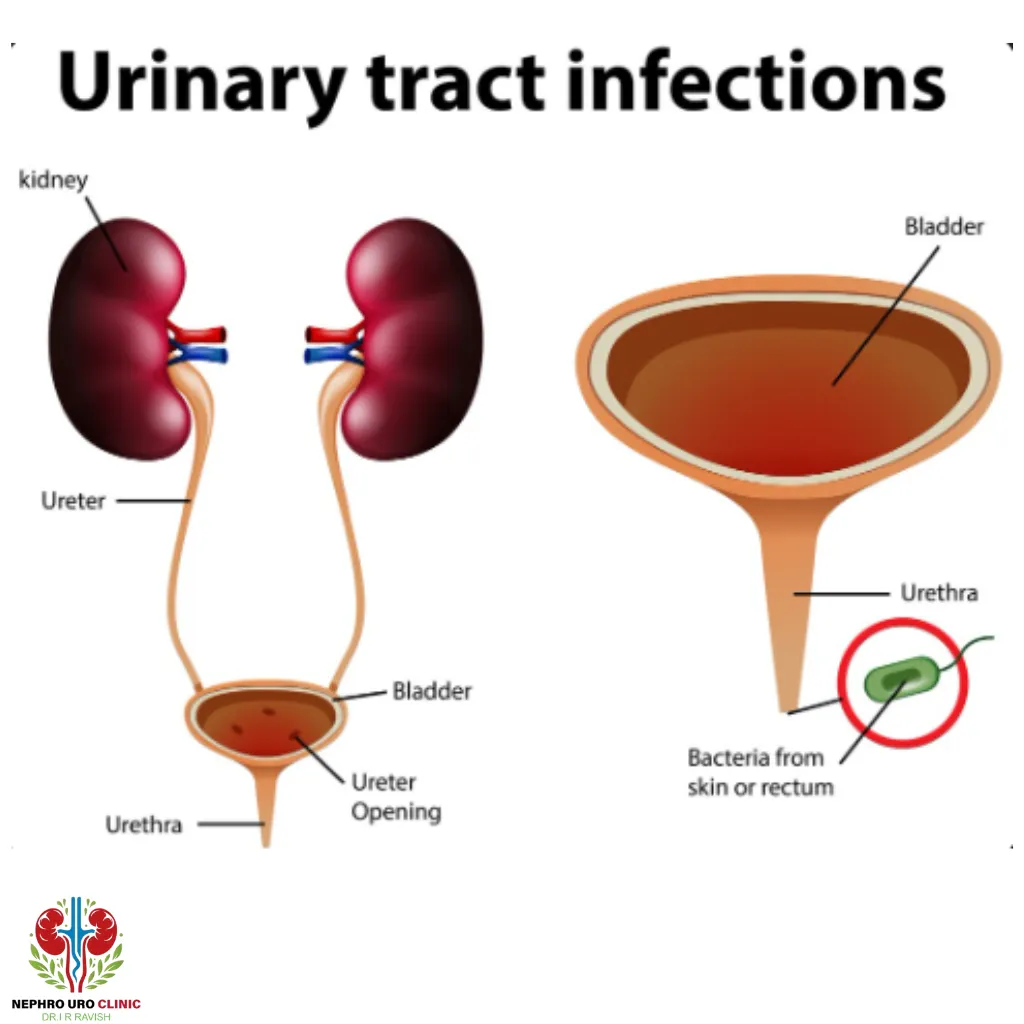
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is a condition where bacteria invade parts of the urinary system—most often the bladder—causing burning sensations, frequent urges to urinate, and pelvic discomfort. While it’s commonly linked to hygiene and sexual activity, a surprising question emerges: can smoking cause a UTI? This isn’t just about lungs anymore. Let’s explore how lighting up a cigarette might be quietly fueling those painful infections.
Can Smoking Cause a UTI?
- Weakened Immune Defense: Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that impair white blood cell function, making it harder for the body to fight off bacteria. This weakened immunity answers the question — can smoking cause a UTI — with a strong yes, as the body becomes less capable of defending the urinary tract.
- Bladder Lining Irritation: Tobacco toxins irritate the bladder wall, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth. This irritation can lead to infections in both men and women, prompting questions like can smoking cause UTI in men and can smoking cause UTI in women — both of which are rooted in the same harmful effect.
- Disruption of Vaginal Flora: In women, smoking disrupts the natural balance of vaginal bacteria and estrogen levels, which protect against UTIs. This imbalance allows harmful bacteria to thrive, directly supporting the link that can smoking cause UTI in women.
- Dehydration and Toxin Concentration: Smokers often suffer from chronic dehydration, which reduces urine output. Less urine means toxins aren’t flushed properly, increasing UTI risk and supporting the concern: does smoking cause UTI in men.
Does Smoking Make UTI Symptoms Worse?
- Prolonged Inflammation and Pain: Smoking intensifies inflammation in the bladder and urinary tract, which can worsen burning sensations, urgency, and abdominal pain. This directly links to the concern: can smoking cause a UTI and aggravate its symptoms once the infection starts.
- Delayed Healing Response: Cigarette chemicals slow tissue repair and reduce oxygen supply to affected areas. When UTIs occur, the body struggles to heal, raising the concern can smoking cause kidney disease through repeated or prolonged infections.
- Increased Antibiotic Resistance: Smokers may respond poorly to antibiotic treatment due to compromised immunity and recurring infection. This resistance can prolong UTI symptoms, making treatment less effective and increasing long-term health risks.
- Deeper Organ Involvement: Continued smoking may push UTIs beyond the bladder to the kidneys. This escalation adds weight to the question: can smoking cause kidney disease, especially in chronic cases where infections go untreated.
How Smoking Affects the Urinary Tract and Bladder
- Direct Chemical Damage to the Bladder Wall: The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke are filtered through the kidneys and stored temporarily in the bladder. These substances irritate and damage the bladder lining, increasing vulnerability to infections — directly supporting the concern: can smoking cause a UTI.
- Reduced Blood Flow to the Urinary Tract: Nicotine constricts blood vessels, lowering blood flow to the bladder and urethra. This limits oxygen and nutrient delivery, slowing tissue repair. For men especially, this explains how smoking can cause UTI in men by compromising urinary tract resilience.
- Altered Urine pH Levels: Smoking may lead to acidic urine, which disrupts the bladder’s microbial defense. This change creates an environment in which bacteria thrive, increasing the likelihood of UTIs in both men and women.
- Increased Risk of Bladder Cancer and Chronic Infections: Smoking is a leading cause of bladder cancer, but before that stage, it often leads to chronic bladder inflammation and recurring infections — reinforcing how deeply can smoking cause a UTI and long-term urinary issues.
The Effects of Smoking on UTI Treatment and Recovery
- Slower Immune Response: When fighting off a UTI, the body depends on a strong immune system. Smoking dulls immune cell activity, making it harder to eliminate the infection. This is particularly concerning when considering can smoking cause a UTI and then delay its healing.
- Frequent Recurrences in Women: Can smoking cause UTI in women? Yes, and it also makes them more likely to experience recurrent infections. The constant irritation and disruption to protective vaginal flora reduce the effectiveness of standard treatment.
- Reduced Drug Absorption: Smoking can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb antibiotics properly. This weakens their effectiveness, allowing the infection to linger or return, especially when combined with poor hydration or ongoing tobacco use.
- Complications in Chronic Cases: Smokers recovering from a UTI often face repeated flare-ups or complications like kidney involvement. This reinforces how smoking not only causes UTIs but also hinders complete recovery, prolonging discomfort and increasing the risk of further urinary damage.
Ways to Manage and Treat UTI if You’re a Smoker
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: Hydration is critical—smokers should drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria and toxins. Reducing caffeine and spicy foods can also soothe the bladder lining and decrease irritation, lowering the risk of infection linked to the question: can smoking cause a UTI.
- Bladder Health Supplements: Cranberry extract, D-mannose, and probiotics support bladder and urinary health. These supplements can help restore bacterial balance and strengthen the urinary tract, offering extra protection for those wondering does smoking cause UTI in men and seeking preventive solutions.
- Bladder Protection Products: Products like pH-balanced feminine washes, cotton underwear, and moisture-wicking clothing help prevent bacterial growth. Smokers should be extra cautious, especially since can smoking cause a UTI is strongly tied to external irritants and lifestyle triggers.
- Routie Medical Monitoring: Smokers are encouraged to undergo regular urine tests or screenings for bladder health. Catching early signs of UTI or inflammation allows timely treatment and may help prevent serious infections, especially in those asking does smoking cause UTI in men repeatedly.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking for UTI Patients
- Improved Immune Function: Quitting allows white blood cells to recover, improving the body’s ability to fight infections. This reduces both the frequency and intensity of UTIs, answering the concern: can smoking cause a UTI with a positive outlook post-quitting.
- Better Kidney and Bladder Health: Smoking cessation restores blood flow and reduces inflammation in the urinary system. For those wondering how does smoking affect kidney disease, stopping the habit can significantly reduce long-term risks and slow progression.
- Enhanced Treatment Response: Antibiotics work more effectively in non-smokers, leading to quicker UTI recovery. Healing is faster and more complete without nicotine interfering with the body’s natural repair mechanisms.
- Stabilized Vaginal Flora and Hormones in Women: Women experience a natural rebalancing of protective bacteria and estrogen levels after quitting. This reduces the chance of recurrent UTIs, supporting recovery and long-term urinary tract health.
Tips to Quit Smoking and Lower Your Risk of UTI
- Gradual Nicotine Reduction: Instead of quitting abruptly, reduce nicotine intake slowly through patches, lozenges, or gum. This method lessens withdrawal and helps the body begin healing — which supports the question how does smoking affect kidney disease, by removing the toxin load more gently.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Increase water intake and consume foods like berries, leafy greens, and garlic to reduce bladder inflammation. This counters the effects tied to does smoking cause UTI in men, helping maintain a cleaner urinary tract.
- Join Support Programs or Counseling: Behavioral therapy and support groups address the emotional side of addiction. Quitting becomes easier with guidance, and as the body heals, it lowers the risk of UTI and chronic kidney conditions — crucial when asking how does smoking cause kidney disease.
- Create Smoke-Free Spaces: Removing smoking triggers at home or work reinforces change. Fewer cues mean fewer relapses and a healthier bladder environment, ultimately protecting the urinary system and reducing UTI risk linked to smoking.
Conclusion
Smoking doesn’t just affect the lungs—it impacts the urinary system in multiple harmful ways. From weakening immunity to damaging bladder tissues, the evidence is clear that smoking raises UTI risk in both men and women. Recovery becomes harder, and complications more likely.
Break the cycle. Choose your health. Stop smoking to protect your bladder, kidneys, and overall well-being.




